Welcome to our article on the difference between a low-glycemic diet and a high-protein diet. These two popular nutrition approaches offer unique benefits and have distinct effects on our bodies. In this section, we will explore the key differences between these diets, including their focus on the glycemic index, protein intake, and their impact on overall health and weight management.
Key Takeaways:
- A low-glycemic diet prioritizes foods with a low glycemic index, which have minimal impact on blood sugar levels.
- A high-protein diet emphasizes consuming protein-rich foods to support muscle growth and satiety.
- Low-glycemic diets are beneficial for blood sugar control, weight management, and reducing the risk of chronic diseases.
- High-protein diets can aid in weight loss, boost metabolism, preserve lean muscle mass, and promote satiety.
- Choosing the right diet depends on individual goals, preferences, and health conditions, and consulting a healthcare professional or dietitian is recommended.
Understanding the Low-Glycemic Diet
A low-glycemic diet is centered around consuming foods with a low glycemic index (GI). The glycemic index ranks carbohydrates based on their impact on blood sugar levels. Foods with a low GI are slowly digested and absorbed, resulting in a gradual rise in blood sugar.
Low-glycemic foods include whole grains, fruits, vegetables, and legumes. These foods provide sustained energy and help stabilize blood sugar levels. By choosing low-glycemic options, individuals can avoid the spikes and crashes in blood sugar that can occur with high-glycemic foods, such as sugary snacks and refined carbohydrates.
A low-glycemic diet offers several health benefits. One of the key advantages is improved blood sugar control. The gradual release of sugar into the bloodstream helps prevent sudden spikes and falls in blood glucose levels, which can be particularly beneficial for individuals with diabetes or those at risk of developing the condition.
Additionally, a low-glycemic diet has been associated with better weight management. These foods tend to be more filling due to their fiber content, promoting satiety and reducing the likelihood of overeating. By choosing low-glycemic options, individuals can support their weight loss efforts and maintain a healthy body weight.
| Health Benefits of a Low-Glycemic Diet |
|---|
| Improved blood sugar control |
| Better weight management |
| Reduced risk of chronic diseases |
| Increased satiety |
In summary, the low-glycemic diet focuses on consuming foods with a low glycemic index to stabilize blood sugar levels and promote overall health. By incorporating whole grains, fruits, vegetables, and legumes into their diet, individuals can reap the benefits of improved blood sugar control, enhanced weight management, and reduced risk of chronic diseases.
Exploring the High-Protein Diet
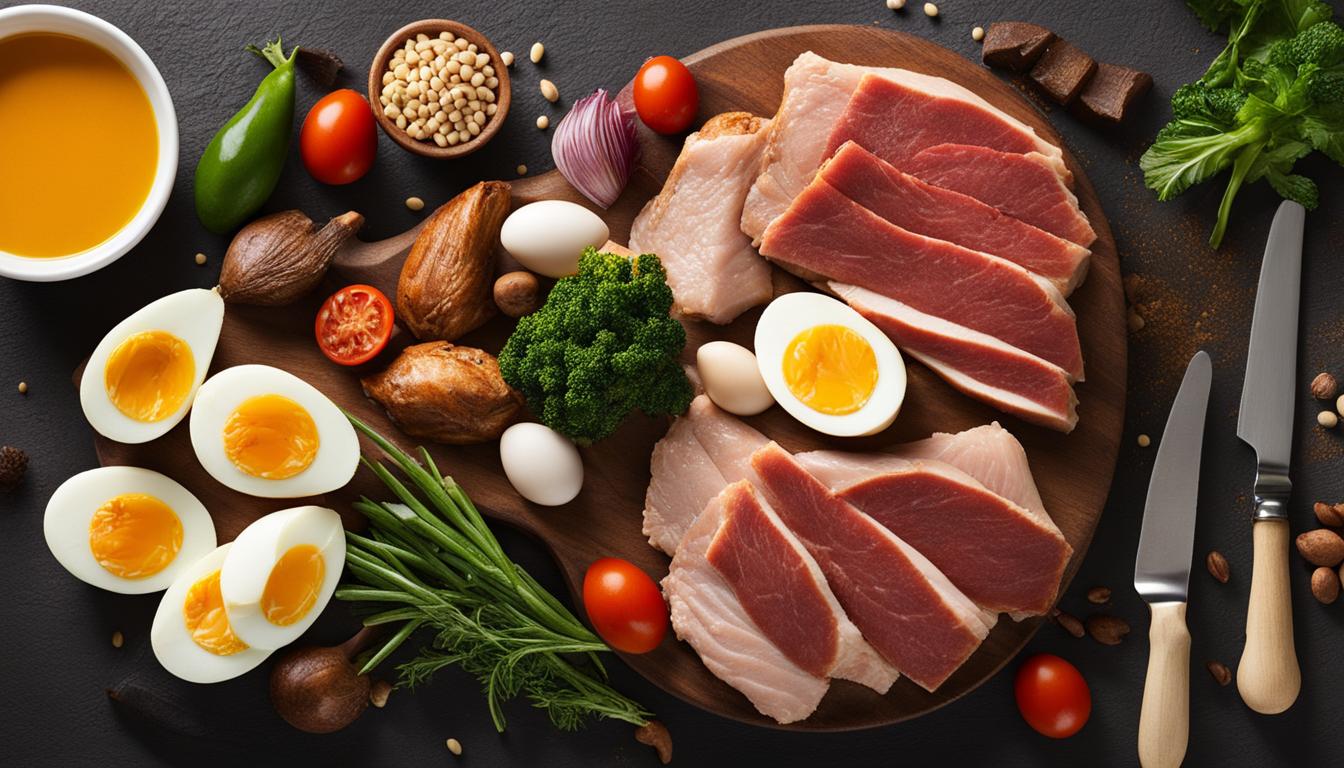
A high-protein diet is centered around consuming foods that are rich in protein. Protein plays a crucial role in building and repairing tissues, supporting muscle growth, and promoting satiety. By increasing protein intake, individuals following a high-protein diet aim to optimize these benefits and potentially enhance weight loss efforts.
Common high-protein foods include meat, poultry, fish, dairy products, legumes, and tofu. These foods provide ample amounts of protein and can be incorporated into various meals and snacks. For individuals who prefer animal-based protein sources, options such as lean cuts of beef or chicken breasts can be included in a high-protein meal plan. Alternatively, plant-based protein sources like lentils or quinoa provide a suitable alternative for vegetarians or vegans.
A high-protein diet is often favored for weight loss due to its ability to curb appetite and boost metabolism. Protein has a higher thermic effect, meaning that more calories are burned during the digestion and absorption process compared to carbohydrates or fats. Additionally, consuming adequate protein can help preserve lean muscle mass during weight loss, ensuring that the majority of weight loss comes from fat rather than muscle.
Table: High-Protein Foods
| Animal-Based Protein Sources | Plant-Based Protein Sources |
|---|---|
| Lean cuts of beef | Lentils |
| Chicken breasts | Quinoa |
| Fish (salmon, tuna) | Chickpeas |
| Eggs | Tofu |
| Greek yogurt | Edamame |
It is essential to note that while a high-protein diet can be effective for weight loss, it should be balanced with other essential nutrients. Incorporating a variety of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and healthy fats is necessary to ensure overall nutritional adequacy. Additionally, consulting with a healthcare professional or registered dietitian can provide personalized guidance and help tailor a high-protein meal plan to an individual’s specific needs and goals.
Key Differences Between Low-Glycemic and High-Protein Diets
When it comes to choosing the right diet, understanding the key differences between low-glycemic and high-protein diets can help you make an informed decision. These diets vary in terms of their approach to nutrient composition, effects on blood sugar levels, and impact on satiety.
Glycemic Load
A major distinction between the two diets lies in the consideration of glycemic load. While a low-glycemic diet focuses on the glycemic index of foods, which measures how quickly they raise blood sugar levels, a high-protein diet may not take this into account. By factoring in the quantity of carbs consumed, the glycemic load reflects a more comprehensive view of a food’s effect on blood sugar. Therefore, a low-glycemic diet not only focuses on the type of carbohydrates but also takes into account portion sizes and overall carb intake.
Nutrient Composition
Low-glycemic diets emphasize whole, nutrient-dense foods such as whole grains, fruits, vegetables, and legumes. These foods provide essential vitamins, minerals, and fiber, contributing to overall health and wellbeing. On the other hand, high-protein diets prioritize protein-rich foods like meat, poultry, fish, and dairy products. While protein is crucial for muscle growth and repair, it’s important to ensure a balance of other nutrients as well.
Satiety
Both low-glycemic and high-protein diets can contribute to increased satiety, but through different mechanisms. Low-glycemic foods are digested more slowly, leading to a gradual release of energy and a longer-lasting feeling of fullness. High-protein foods, on the other hand, have a high thermic effect, meaning they require more energy to digest, which can also contribute to a sense of satisfaction and reduced appetite.
| Low-Glycemic Diet | High-Protein Diet | |
|---|---|---|
| Nutrient Composition | Emphasizes whole, nutrient-dense foods | Prioritizes protein-rich foods |
| Glycemic Load | Takes into account both glycemic index and carb quantity | May not consider glycemic load |
| Satiety | Provides gradual release of energy and longer-lasting fullness | Has a high thermic effect and can reduce appetite |
Health Benefits of Both Diets
Both the low-glycemic and high-protein diets offer a range of health benefits. A low-glycemic diet has been shown to have positive effects on blood sugar control, making it particularly beneficial for individuals with diabetes or those at risk of developing chronic diseases. By focusing on consuming foods with a low glycemic index, this diet can help stabilize blood sugar levels and reduce the risk of insulin resistance.
Additionally, a low-glycemic diet has been associated with weight management and improved satiety. The slow digestion and absorption of low-glycemic foods provide a steady release of energy, which can help control hunger and prevent overeating. This can be especially advantageous for individuals looking to lose weight or maintain a healthy weight.
On the other hand, a high-protein diet has its own set of health benefits, particularly when it comes to weight loss. By increasing protein intake and reducing carbohydrates and fats, this diet can promote satiety, boost metabolism, and preserve lean muscle mass. The higher protein content of this diet can also support muscle growth and repair, improve body composition, and enhance exercise performance.
It’s important to note that the health benefits of both diets may vary depending on individual needs, preferences, and health conditions. Consulting a healthcare professional or registered dietitian is recommended to determine which diet is most suitable for an individual’s specific goals and requirements.

Conclusion
In conclusion, both the low-glycemic diet and the high-protein diet offer a range of health benefits and can be effective for weight management. The low-glycemic diet focuses on stabilizing blood sugar levels and is particularly beneficial for individuals with diabetes or those at risk of chronic diseases. By consuming whole, nutrient-dense foods with a low glycemic index, this diet can help improve blood sugar control, promote satiety, manage weight, and reduce the risk of conditions like type 2 diabetes and heart disease.
On the other hand, the high-protein diet emphasizes protein-rich foods to support muscle growth, preserve lean muscle mass, and promote satiety. This diet can be an effective tool for weight loss, as it boosts metabolism, reduces appetite, and helps achieve a healthy body composition. Additionally, it can enhance exercise performance and support muscle repair and recovery.
Ultimately, the choice between a low-glycemic diet and a high-protein diet depends on individual goals, preferences, and health conditions. It is essential to consult with a healthcare professional or a registered dietitian to receive personalized guidance and determine which approach is most suitable for your specific needs. Whether you opt for the low-glycemic diet or the high-protein diet, both can provide valuable strategies for improving your health and managing your weight effectively.
FAQ
What is a low-glycemic diet?
A low-glycemic diet focuses on consuming foods with a low glycemic index, which have minimal impact on blood sugar levels.
What are some examples of low-glycemic foods?
Examples of low-glycemic foods include whole grains, fruits, vegetables, and legumes.
How does a low-glycemic diet benefit health?
A low-glycemic diet can improve blood sugar control, aid in weight management, and reduce the risk of chronic diseases like diabetes and heart disease.
What is a high-protein diet?
A high-protein diet emphasizes consuming foods that are rich in protein to support muscle growth and satiety.
What are some examples of high-protein foods?
Examples of high-protein foods include meat, poultry, fish, dairy products, legumes, and tofu.
How does a high-protein diet help with weight loss?
A high-protein diet can curb appetite, boost metabolism, preserve lean muscle mass, and promote weight loss.
What are the key differences between low-glycemic and high-protein diets?
Low-glycemic diets focus on the glycemic index of foods and their impact on blood sugar levels, while high-protein diets prioritize protein intake and its effects on satiety and muscle preservation.
What is the glycemic load?
The glycemic load considers both the glycemic index and the quantity of carbs consumed in a food.
What health benefits do low-glycemic and high-protein diets offer?
Low-glycemic diets can improve blood sugar control, aid in weight management, and reduce the risk of chronic diseases. High-protein diets can promote satiety, preserve muscle mass, and support weight loss.
Which diet is right for me?
The choice between a low-glycemic and high-protein diet depends on individual goals, preferences, and health conditions. It’s best to consult a healthcare professional or registered dietitian for personalized guidance.
 Skip to main content
Skip to main content